AiTM Phishing: How Attackers Use Session-Token Theft to Bypass MFA in Microsoft 365 — Detection and Prevention
Adversary-in-the-Middle (AiTM) phishing presents a sophisticated threat to Microsoft 365 users by subverting multi-factor authentication (MFA). This article explores how attackers exploit session-token theft to bypass MFA, highlights detection signals and containment strategies, and outlines robust prevention controls for IT teams. We close with practical next steps to neutralize this evolving attack vector.
🔍 How AiTM Phishing and Session-Token Theft Defeat MFA
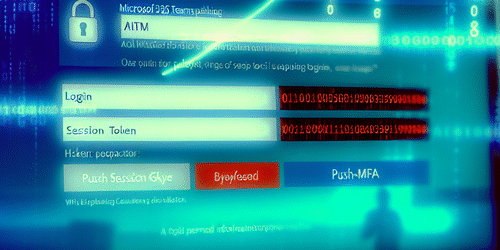
AiTM phishing attacks exploit vulnerabilities in MFA by placing a proxy between users and legitimate services, intercepting authentication flows in real time. Rather than stealing static passwords or one-time codes, attackers harvest session tokens, such as cookies or OAuth tokens, that serve as valid authentication artifacts granting access without triggering MFA challenges.
Tools like Evilginx operate as transparent proxies, relaying credentials and MFA responses from the user to the service. Upon successful authentication, session tokens returned by the service are captured by the attacker. These tokens can then be replayed to impersonate the user’s authenticated session directly, bypassing any additional MFA enforcement since the original login process was already validated.
This mechanism differs fundamentally from credential replay attacks. Token replay abuses valid session artifacts, meaning attackers don’t need to repeatedly supply passwords or OTPs, making detection by traditional MFA controls difficult. Since many MFA methods, including SMS OTP or app prompts, secure only the initial login authentication and not the session itself, stolen tokens grant persistent and stealthy access until they expire or are revoked.
AiTM proxies commonly modify HTTP headers slightly, introduce minimal latency, and mimic legitimate user-agent strings to avoid suspicion. Because the attacker intermediates and seamlessly captures MFA responses, SMS or OTP-based MFA often fails to protect against these session-token theft attacks.
Microsoft Security Blog
⚠️ Attack Indicators: Telemetry Signals That Suggest Token Theft or AiTM Activity
Detection hinges on identifying unusual authentication telemetry in Microsoft 365 and security information event management (SIEM) systems. Security teams should look for high-confidence indicators associated with session token replay and AiTM phishing campaigns:
- Anomalous session start times: Sessions initiating outside normal user hours or unusual patterns not aligned with typical behavior
- Header anomalies: HTTP headers with missing or inconsistent user-agent strings, inconsistent with the user’s usual devices
- Token reuse across IPs/UA: Identical session tokens or cookies observed from multiple disparate IP addresses or device user agents
- Multiple concurrent sessions with same tokens: Unexpected simultaneous authentications using the same session token
Effective detection involves correlating sign-in logs with token activity and spotting behavioral deviations. Organizations can operationalize threat hunting by using sample Kusto Query Language (KQL) queries within Microsoft Sentinel or Azure AD logs to identify suspicious sign-ins, such as rapid MFA challenge completions from new or anonymized IP addresses.
Continuous telemetry monitoring accelerates AiTM phishing identification and token theft alerts, decreasing attacker dwell time and enhancing incident response capabilities.
Microsoft Docs – Sign-in Risk Detection
🛡️ Short-Term Containment & Incident Response Playbook for Token Theft
When token theft or AiTM phishing activity is suspected, immediate containment and structured response minimize damage and support forensic investigation:
- Revoke all active sessions and tokens: Use Entra ID portal or PowerShell commands to invalidate sessions, forcing re-authentication and rendering stolen tokens useless
- Block compromised devices and suspicious IPs: Enforce Conditional Access policies and network restrictions to halt attacker presence
- Collect forensic evidence: Preserve audit logs, session tokens, and telemetry for investigation and compliance
- Communicate incidents quickly: Notify users and security teams with clear guidance on password resets and MFA re-enrollment
- Perform credential resets: Enforce password changes and transition to phishing-resistant authentication
- Monitor for recurrence: Heighten logging and detection sensitivity for related anomalies
Coordinate with incident response teams and legal counsel to manage escalation and compliance requirements. Careful rollback strategies are crucial to avoid disrupting legitimate users while neutralizing threats.
Microsoft Security Incident Response Guide
🔐 Medium- and Long-Term Prevention: Entra ID & Microsoft 365 Controls to Block Token Theft
Organizations must implement layered and robust controls to defend against AiTM phishing and session-token theft:
- Enforce phishing-resistant authentication: Use FIDO2 security keys or certificate-based authentication (CER) that are immune to proxy phishing
- Implement Conditional Access policies: Require evaluation of session risk, device compliance, and network location as access conditions
- Configure strict session controls: Minimize token lifetimes, require frequent sign-in challenges, and enable Continuous Access Evaluation (CAE) to revoke sessions in near real-time
- Adopt security defaults and baseline configurations: Utilize Microsoft’s recommended security baselines to maintain strong default posture
- Deploy Identity Protection risk policies: Automatically block or require additional verification for risky sign-ins based on risk detection
These steps harden the authentication infrastructure, drastically limiting attackers’ options to steal and reuse session tokens.
Microsoft Docs – Identity Protection
🚀 Practical Next Steps, Playbooks & Resources for IT Teams (What to Deploy This Week)
IT teams should prioritize rapid deployment of key mitigations over the coming weeks to neutralize AiTM phishing risks:
- Deploy detection queries: Implement provided KQL templates in Microsoft Sentinel or Azure AD logs to hunt for suspicious token reuse and anomalous sign-ins
- Implement Conditional Access templates: Enforce phishing-resistant MFA and session controls immediately
- Run emergency response scripts: Automate session revocation, token invalidation, and device blocking using PowerShell
- Enable Continuous Access Evaluation: Apply CAE on critical cloud applications to ensure real-time token revocation upon risk detection
- Educate end users: Launch awareness programs focusing on AiTM phishing risks and promote hardware FIDO2 security key adoption
- Subscribe to threat intelligence feeds: Utilize Microsoft Defender and third-party intel services to stay informed on emergent AiTM campaigns
By following authoritative Microsoft Security Documentation, Entra ID best practices, and Microsoft Sentinel hunting playbooks, IT teams can effectively respond to active threats while building durable resilience.
Microsoft Security Incident Response Resources